Metabolism is a complex and essential physiological process within the human body that plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy weight. When the metabolism functions optimally, it efficiently converts the calories from the food we eat into energy, which helps with weight management and overall well-being. On the other hand, if the metabolism is slow, it can lead to weight gain and contribute to various health issues. The metabolism process is influenced by a combination of factors, including genetic predispositions, changes that occur with age, the activity of the thyroid gland, the composition of muscle mass, and hormonal regulation. All these factors interact in intricate ways to determine how efficiently our bodies use and store energy. In this comprehensive blog post, we will delve deep into the scientific intricacies of metabolism, shedding light on its profound impact on body weight and overall health. By understanding the underlying mechanisms of metabolism, readers can gain valuable insights into fostering a balanced approach to weight management and overall well-being.
Introduction to Metabolism and Its Role in Body Weight Regulation
Metabolism is a fundamental biological process encompassing a series of intricate chemical reactions that sustain life and enable bodily functions. Within this process, food undergoes breakdown, resulting in the conversion of nutrients into energy, which is further utilized for various physiological activities, including generating heat and facilitating movement. The paramount significance of metabolism lies in its profound impact on body weight regulation, as it governs the rate at which the body expends calories. Metabolism encompasses not only the breakdown of food and energy conversion but also other essential functions, such as cellular maintenance and repair, hormone synthesis, and waste elimination. At its core, metabolism ensures that the nutrients we consume are transformed into the energy needed for our bodies to function optimally. This process not only supports vital bodily functions but also influences our weight. The rate at which we burn calories, known as the metabolic rate, plays a pivotal role in determining whether we gain, lose, or maintain weight.
By comprehending the nuances of metabolism, we can gain a deeper understanding of how it influences our body weight and lays the foundation for implementing effective strategies to manage weight and foster a healthy lifestyle.
Metabolism: Breaking Down the Basics
Metabolism is a sophisticated process that can be dissected into two main components: catabolism and anabolism. Catabolism entails the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy in the process. On the other hand, anabolism involves the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler building blocks, requiring energy for this constructive process. In simple terms, catabolism is like the body's energy-releasing "breaking down" phase, while anabolism is the energy-consuming "building up" phase. Together, these processes regulate the energy balance within the body. The metabolic rate denotes the speed at which the body expends calories to transform food into usable energy. A higher metabolic rate signifies an increased calorie-burning capacity, which can contribute to weight loss as the body efficiently utilizes stored energy. Conversely, a slower metabolic rate results in reduced calorie expenditure, potentially leading to weight gain as surplus energy is stored in the body. Understanding the delicate interplay between catabolism, anabolism, and metabolic rate provides valuable insights into the mechanisms underpinning weight fluctuations, empowering individuals to make informed choices to achieve their weight management goals.
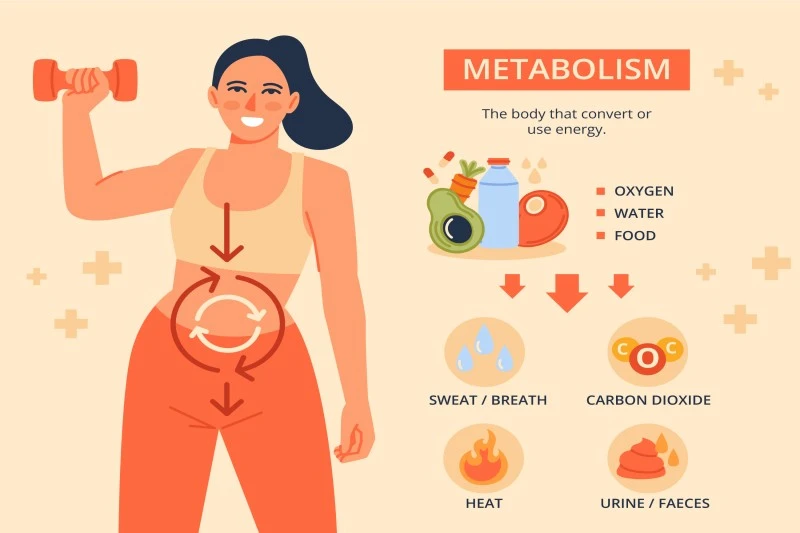
BMR vs. RMR: Understanding Basal Metabolic Rate and Resting Metabolic Rate
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) and Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) are fundamental components of the body's energy expenditure during periods of rest. BMR represents the number of calories the body consumes while at complete rest solely to maintain essential bodily functions like breathing, circulation, and cellular processes. On the other hand, RMR includes the calories burned during rest while lying down and awake, but not in a completely rested state like BMR. Both BMR and RMR are influenced by various factors, such as age, gender, body composition (muscle mass and fat percentage), and genetics, leading to individual variations. Accurate measurement of BMR and RMR is crucial for establishing a reliable foundation for personalized dietary and exercise plans. Healthcare professionals often use methods like indirect calorimetry to obtain precise measurements, which involve analyzing the amount of oxygen consumed and carbon dioxide produced during rest.
It's important to distinguish between BMR and RMR, as BMR is typically measured under controlled conditions, such as in the early morning after an overnight fast and abstaining from exercise. On the other hand, RMR can be measured at any time during the day under normal living conditions without the need for controlled fasting or specific timeframes. Understanding these differences helps healthcare professionals and individuals determine their daily caloric needs, making it a valuable tool in weight management efforts.
It's important to acknowledge that BMR and RMR can significantly vary between individuals due to inherent physiological differences. This highlights the significance of personalized assessments to provide accurate and tailored recommendations for dietary and exercise interventions. Individuals can make informed decisions to support their weight management efforts and overall health by understanding the factors influencing these metabolic rates.
The Factors Influencing Metabolism: From Genetics to Age
Metabolism, a finely tuned biological process, is subject to influence from a diverse array of factors, encompassing genetics, age, and gender. Individual genetic makeup plays a significant role, leading to natural variations in metabolic rates, resulting in some individuals enjoying a faster metabolism while others may experience a slower one. Genetic studies have revealed that certain metabolism-related genes, such as energy expenditure and fat storage, can impact an individual's metabolic efficiency.
Moreover, as individuals age, metabolic activity tends to decelerate, decreasing the rate at which calories are burned. This age-related decline in metabolism is partly attributed to changes in hormonal regulation and the loss of lean muscle mass. Consequently, older individuals generally exhibit a slower metabolism than their younger counterparts, making weight management more challenging as they age.
Aside from genetics and age, several other lifestyle and environmental factors can impact metabolism. Chronic stress, for instance, can disrupt hormonal balance and contribute to alterations in metabolic function. The release of stress hormones, such as cortisol, can influence how the body uses and stores energy, potentially leading to weight gain and metabolic imbalances.
Additionally, the quality and duration of sleep can influence metabolism, with inadequate sleep potentially leading to disturbances in metabolic processes. Sleep deprivation is associated with insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism, adversely affecting weight and overall metabolic health.
Physical activity level also plays a pivotal role in metabolism, as regular exercise can bolster metabolism by promoting lean muscle mass, which requires more energy for maintenance. While resistance training can indeed increase muscle mass and metabolism, it's essential to emphasize that overall weight management and health depend on a combination of factors, including diet, aerobic exercise, and lifestyle habits. Relying solely on muscle-building exercises without considering other factors may not lead to significant weight loss or overall well-being.
Furthermore, lifestyle choices, such as smoking, can detrimentally affect metabolism. Smoking can lead to a decrease in appetite and disrupt the body's ability to metabolize nutrients, leading to potential weight gain efficiently. The harmful compounds in cigarettes can also cause oxidative stress, negatively impacting the body's metabolic processes.
By adopting a holistic approach that addresses both genetic predispositions and lifestyle choices, individuals can foster a balanced metabolism and enhance overall well-being.
How Metabolism Changes with Weight Loss and Weight Gain
Metabolism undergoes dynamic adjustments in response to changes in body weight, and this interplay plays a pivotal role in weight management. When individuals embark on a weight loss journey, their metabolism tends to slow down, reducing the number of calories burned. This decrease in metabolic rate occurs as the body adapts to the lower caloric intake, seeking to conserve energy and maintain vital bodily functions. Consequently, weight loss can become progressively challenging as the body becomes more efficient in utilizing available energy resources.
Conversely, when individuals gain weight, their metabolism often speeds up to accommodate the increased energy demands associated with the higher body weight. As the body accumulates additional mass, sustaining the augmented physiological workload necessitates more energy. This elevated metabolic rate aids in meeting the energy requirements of the increased body mass.
However, the impact of these metabolic adaptations poses a challenge to sustainable weight management. As people lose weight and their metabolism slows down, it becomes easier to regain lost weight because the body now requires fewer calories to maintain its reduced size. This phenomenon, commonly known as "weight loss plateau," can frustrate weight loss efforts and contribute to weight regain if individuals revert to their previous dietary and lifestyle habits.
Sustainable weight loss entails not only the reduction of calorie intake but also the incorporation of regular physical activity and the development of healthy habits to address the intricacies of metabolism. By embracing a comprehensive approach, individuals can navigate the challenges associated with metabolic adaptations and foster lasting success in achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
Thyroid Hormones and Their Impact on Metabolism and Body Weight
The thyroid gland plays a central role in regulating the body's metabolism through the secretion of essential hormones. Thyroid hormones, including thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), exert powerful effects on various metabolic processes, influencing energy expenditure and overall body weight.
When the thyroid gland becomes overactive, a condition known as hyperthyroidism, it releases excessive thyroid hormone into the bloodstream. This surge in thyroid hormones accelerates the metabolic rate, causing the body to burn calories faster. As a result, individuals with hyperthyroidism may experience unintentional weight loss, even with increased appetite and food intake.
Conversely, an underactive thyroid gland, referred to as hypothyroidism, leads to reduced production of thyroid hormones. This deficiency results in a slowdown of the body's metabolic rate, decreasing calorie expenditure. Consequently, people with hypothyroidism may experience unexplained weight gain or find it challenging to lose weight, despite adhering to a healthy diet and exercise regimen.
Management of thyroid-related metabolic imbalances typically involves medication to restore the appropriate levels of thyroid hormones. Medications or other treatments are used for hyperthyroidism to normalize thyroid hormone levels and alleviate the associated symptoms. In cases of hypothyroidism, hormone replacement therapy is administered to supplement the deficient thyroid hormones and restore metabolic function. Individuals with concerns about thyroid-related metabolic imbalances should consult a healthcare professional for appropriate evaluation and treatment. Self-diagnosis or self-medication should be avoided, and accurate diagnosis is crucial for optimizing metabolic health and achieving effective weight management.
Muscle Mass and Metabolism: The Muscle Metabolic Advantage
Muscle mass is a key determinant in metabolism, presenting a significant advantage due to its higher calorie-burning capacity than fat tissue. The metabolic disparity between muscle and fat tissue is why individuals with more muscle mass typically exhibit a faster metabolism than those with less muscle mass. Muscle tissue necessitates more energy to maintain its structure and functionality, leading to a greater calorie expenditure even during rest periods.
Incorporating resistance training exercises, such as weightlifting, into one's fitness routine holds immense potential for enhancing muscle mass and, in turn, boosting metabolism. These activities prompt the muscles to adapt and grow, increasing lean muscle mass. As the muscle mass expands, the body's metabolic rate escalates, facilitating a more efficient utilization of calories for sustaining muscle tissue.
The relationship between muscle mass and metabolism underscores the significance of incorporating strength training exercises into a well-rounded fitness regimen. By enhancing muscle mass through resistance training, individuals can elevate their basal metabolic rate, contributing to overall calorie expenditure even when not actively engaged in exercise. This advantageous effect becomes particularly crucial for those seeking effective weight management or the maintenance of a healthy weight.
Combining resistance training, cardiovascular exercises, and a balanced diet supporting muscle growth can optimize muscle metabolic advantage. This holistic approach enhances metabolism and fosters physical strength, body composition, and metabolic health. By harnessing the muscle metabolic advantage, individuals can embark on a journey of improved fitness, vitality, and long-term well-being.

The Connection Between Diet, Exercise, and Metabolism
The intricate relationship between diet, exercise, and metabolism is pivotal in effective weight management and overall metabolic health. A well-balanced and nutritious diet forms the foundation for supporting metabolism by providing the body with essential nutrients required for optimal functioning. Consuming a healthy diet rich in protein, fiber, and whole grains can be particularly beneficial in boosting metabolism. Protein aids in the repair and growth of tissues, including muscle tissue, while fiber supports digestion and nutrient absorption. Whole grains offer a sustained energy source associated with improved metabolic outcomes.
However, diet alone cannot fully optimize metabolism. Regular exercise constitutes another indispensable component of the equation. Physical activity, such as aerobic exercises and resistance training, contributes to various metabolic benefits. Firstly, exercise fosters the development of lean muscle mass, which, as previously explained, possesses a higher calorie-burning capacity than fat tissue. This increase in muscle mass elevates the basal metabolic rate, leading to a more efficient calorie expenditure even during rest periods.
Secondly, exercise directly burns calories during the activity, aiding in weight management by promoting energy expenditure. Furthermore, regular exercise enhances cardiovascular health, improves insulin sensitivity, and positively influences hormone regulation, all of which play significant roles in metabolism and overall metabolic health.
Metabolism-Boosting Foods: Separating Fact from Fiction
The internet is flooded with information about so-called "metabolism-boosting" foods, but it is essential to discern fact from fiction. While certain foods, such as green tea and chili peppers, have been associated with a slight impact on metabolism, it is crucial to understand that there are no magical solutions for weight loss solely based on specific foods.
While green tea has been shown to contain catechins, which may have a minor effect on metabolism and chili peppers may temporarily increase metabolic rate due to their capsaicin content, these effects are relatively modest and should not be relied upon as a primary strategy for weight loss.
Instead, the most effective approach for boosting metabolism and maintaining a healthy weight is adopting a balanced diet incorporating various nutrient-rich foods. A diet high in protein, fiber, and whole grains provides the body with essential nutrients while promoting satiety, aiding in the management of food intake, and supporting overall health.
Protein is crucial for repairing and building tissues, including muscle tissue, which, as discussed earlier, contributes to an elevated metabolic rate. Fiber aids digestion, helps regulate blood sugar levels, and promotes a feeling of fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating. Whole grains offer a steady energy source, supporting sustained physical activity and overall metabolic function.
Individuals can foster a healthy metabolism, sustainable weight management, and overall well-being by focusing on a well-rounded and balanced diet. The key to success lies in adopting a comprehensive approach encompassing healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, and mindful lifestyle choices.

Can You Really "Boost" Your Metabolism? The Truth Unveiled
The quest for a "boosted" metabolism and quick fixes for long-term weight loss often leads to misconceptions and misinformation. In reality, there is no magical solution to dramatically enhance metabolism permanently. While certain temporary measures, such as consuming caffeine or spicy foods, may induce minor and short-lived increases in metabolic rate, these effects are insufficient for sustainable weight loss or significant metabolic improvements.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle encompassing various interconnected factors is the most effective and lasting approach to supporting metabolism. Regular physical exercise is a cornerstone for enhancing metabolic health. Engaging in aerobic activities, strength training, or other forms of exercise helps to build lean muscle mass, which, as previously mentioned, contributes to a heightened basal metabolic rate.
Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet that provides the body with the necessary nutrients for optimal functioning is essential. A diet rich in protein, fiber, and whole grains supports metabolism and helps manage food intake, promoting a healthy weight.
Furthermore, addressing stress reduction and ensuring adequate sleep are crucial components of a comprehensive approach to supporting metabolic health. Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that impact metabolism and body weight, while sufficient sleep is essential for metabolic regulation and overall well-being.
The Role of Hormones in Metabolism and Weight Management
Various hormones, such as insulin, cortisol, and leptin, play a critical role in metabolism and weight management. Insulin regulates blood sugar levels, cortisol regulates stress levels, and leptin regulates appetite and metabolism. Hormonal imbalances can cause weight gain and other health problems, so it is essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle supporting hormonal balance.
Hormones wield significant influence over metabolism and weight management, orchestrating intricate processes that impact energy balance and overall health. Several essential hormones play critical roles in these mechanisms, each with distinct functions.
Insulin, produced by the pancreas, is a central player in regulating blood sugar levels. It facilitates glucose uptake from the bloodstream into cells for energy use or storage. An imbalance in insulin levels, as seen in conditions like insulin resistance or diabetes, can disrupt blood sugar regulation and contribute to weight gain.
Cortisol, often called the "stress hormone," is secreted by the adrenal glands in response to stress. While cortisol serves important functions, prolonged or chronic stress can produce excessive cortisol, affecting metabolism and promoting weight gain, particularly around the abdominal area.
Leptin, known as the "satiety hormone," is synthesized by fat cells and plays a crucial role in regulating appetite and metabolism. When adequate fat stores are present, Leptin signals the brain to reduce appetite and increase energy expenditure. However, resistance to leptin or disruptions in its signaling can lead to increased appetite and reduced energy expenditure, potentially contributing to weight gain.
Hormonal imbalances can indeed lead to weight gain and other health problems. Fostering hormonal balance through a healthy lifestyle is crucial to maintain metabolic health and support weight management. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress reduction techniques, and adequate sleep contribute to hormonal equilibrium and overall well-being.
Medical Conditions Affecting Metabolism and Their Influence on Body Weight
Several medical conditions can significantly impact metabolism and lead to weight-related issues. Two prominent examples include diabetes and hypothyroidism. In diabetes, the body struggles to regulate blood sugar levels, leading to either insufficient insulin production (Type 1 diabetes) or ineffective use of insulin (Type 2 diabetes). These disruptions in insulin function can result in altered metabolism and, in some cases, weight gain.
Hypothyroidism, characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, leads to reduced production of thyroid hormones. This hormonal deficiency slows down metabolism, potentially contributing to weight gain and difficulty losing weight.
Addressing these conditions often requires medical treatment, which may involve insulin therapy for diabetes or hormone replacement therapy for hypothyroidism. Healthcare professionals can help regulate metabolism and support weight management by managing these conditions.
Furthermore, other medical conditions, such as Cushing's disease and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), have been linked to metabolic disorders and weight gain. Cushing's disease involves the overproduction of cortisol, leading to metabolic disturbances and weight gain, particularly in the face, neck, and abdomen. PCOS, a hormonal disorder affecting women, can cause insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances, contributing to weight gain and difficulties with weight management.
In these cases, comprehensive medical management is essential to address the underlying metabolic issues and promote healthy weight management. Healthcare professionals can develop personalized treatment plans that address the medical condition and associated weight-related concerns, fostering improved metabolic health and overall well-being.
Metabolism and Age: Navigating Metabolic Changes as You Get Older
As individuals age, they often experience natural changes in their metabolism, which can present challenges in maintaining a healthy weight. One common observation is a gradual slowing down of metabolism, where the body becomes more efficient in utilizing calories. This reduced metabolic rate can result in a lower caloric expenditure, making it easier for older adults to gain weight if their dietary habits and physical activity levels remain unchanged.
However, aging doesn't necessarily mean inevitable weight gain or a decline in metabolic health. There are proactive steps that individuals can take to support a healthy metabolism as they age. Embracing a nutritious diet that is well-balanced, rich in essential nutrients, and appropriate for one's age and activity level is vital. Plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can give the body the necessary nutrients to function optimally.
Regular exercise is equally crucial for sustaining a healthy metabolism throughout the aging process. Engaging in aerobic exercises and strength training can help preserve muscle mass, which plays a pivotal role in metabolism. As discussed earlier, maintaining or increasing muscle mass supports a higher basal metabolic rate, leading to more efficient calorie burning.
Additionally, staying physically active in daily life can make a significant difference in supporting metabolic health. Simple activities like walking, gardening, or taking the stairs can contribute to overall calorie expenditure and help counterbalance the age-related decline in metabolism.
By being proactive and adopting a lifestyle encompassing a nutritious diet and regular physical activity, individuals can navigate the metabolic changes that come with age and promote a healthy weight.
The Impact of Sleep and Stress on Metabolism and Weight
Sleep and stress can have a significant impact on metabolism and weight management. Lack of sleep can cause hormonal imbalances that lead to weight gain, while stress can cause the body to produce cortisol, which can also contribute to weight gain. Practicing stress-reduction techniques and getting adequate sleep can help to support a healthy metabolism and promote weight loss.
Sleep and stress substantially affect metabolism and weight management, highlighting the importance of addressing these factors for overall health. Insufficient sleep can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to increased hunger and reduced satiety hormones, such as ghrelin and leptin. As a result, individuals may experience stronger cravings for unhealthy foods and a decreased ability to recognize when they are full, potentially leading to overeating and mass gainers.
Moreover, chronic stress triggers the release of cortisol, commonly known as the "stress hormone." Elevated cortisol levels can contribute to increased appetite, particularly for high-calorie and sugary foods, and may promote fat storage around the abdominal area. This combination of stress-induced changes in eating behavior and metabolism can contribute to weight gain and difficulties in weight management.
To support a healthy metabolism and promote weight loss, it is essential to adopt strategies that mitigate the impact of sleep and stress on the body. Prioritizing sufficient and restful sleep is crucial for hormonal balance and overall well-being. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to ensure adequate recovery and support metabolic functions.
Additionally, implementing stress-reduction techniques can be highly beneficial. Practices such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature can help manage stress levels and promote relaxation. Reducing stress helps regulate cortisol levels and improves eating habits and overall metabolic health.

Practical Tips for Enhancing Metabolic Health and Weight Management
People can follow many practical tips to enhance their metabolic health and support long-term weight management.
- Adopt a Healthy Diet: Focus on a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. Limit processed foods, sugary snacks, and excessive consumption of high-calorie, low-nutrient foods.
· Regular Exercise: Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine. Aim for a combination of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises to support overall metabolic health. Find activities you enjoy to make exercise a sustainable part of your lifestyle.
· Manage Stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature. High-stress levels can negatively impact metabolism and weight management, so finding ways to de-stress is essential.
· Prioritize Sleep: Make sleep a priority and aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Sufficient sleep supports hormonal balance, appetite regulation, and overall metabolic health.
· Avoid Smoking: If you smoke, seek help to quit smoking. Smoking negatively affects lung health, disrupts metabolism, and contributes to weight gain.
· Limit Alcohol Consumption: Moderate your alcohol intake, as excessive alcohol consumption can add empty calories to your diet and disrupt metabolic processes.
· Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support digestion, metabolism, and overall well-being. Sometimes thirst can be mistaken for hunger, leading to unnecessary calorie consumption.
· Eat Regularly: Avoid skipping meals, which can lead to irregular blood sugar levels and negatively affect metabolism. Eat balanced meals and snacks throughout the day to maintain energy levels and support metabolism.
· Avoid Crash Diets: Avoid extreme and restrictive diets that can negatively impact metabolism and lead to nutrient deficiencies. Instead, focus on long-term, sustainable lifestyle changes.
· Track Progress: Keep a food journal or use a fitness app to track your dietary habits, exercise routine, and weight management progress. This can help you identify areas for improvement and stay motivated on your journey.
By implementing these practical tips, you can enhance your metabolic health, support weight management goals, and improve your overall well-being. Remember that achieving sustainable results takes time and consistency, so be patient and celebrate each small step toward a healthier lifestyle. If you have specific health concerns or weight management challenges, consider consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized guidance and support.
Exercise and Metabolism: Finding the Right Workout for Your Goals
Physical activity plays a pivotal role in boosting metabolism and facilitating weight loss. Certain types of exercise, such as resistance training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT), have been particularly effective in supporting metabolic health and promoting calorie expenditure.
· Resistance Training: Incorporating resistance training exercises, such as weightlifting, bodyweight exercises, or resistance bands, can be highly beneficial for metabolism. These exercises work to build and maintain lean muscle mass, which, as previously discussed, leads to an increased basal metabolic rate and improved calorie burning even at rest. Resistance training also supports bone health, enhances strength, and contributes to a toned and well-defined physique.
· High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): HIIT involves alternating short bursts of intense exercise with periods of rest or lower-intensity activity. This approach challenges the cardiovascular system and triggers an "afterburn" effect known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC). EPOC leads to an increased calorie burn post-workout, further supporting weight loss and metabolism.
It's important to note that while resistance training and HIIT can be highly effective, the right workout routine for you depends on your individual fitness goals, preferences, and physical condition. Some individuals may prefer a mix of different exercises, while others might enjoy and succeed in focusing on a particular type of workout.
In addition to resistance training and HIIT, activities such as aerobic exercises, swimming, dancing, or yoga can also contribute to overall fitness and metabolism. The key is finding activities you enjoy and can sustain over the long term.
Finding the proper workout routine that aligns with your goals and preferences is essential for maintaining consistency and achieving lasting results. If you need help figuring out where to start or have specific fitness objectives, consider seeking guidance from a certified fitness trainer or exercise professional who can design a personalized workout plan tailored to your needs and goals.

Nutrition Strategies to Support a Healthy Metabolism and Body Weight
Adopting a nutritionally balanced diet is a cornerstone of supporting a healthy metabolism and achieving long-term weight management. The focus should be on incorporating nutrient-dense foods that provide essential nutrients while promoting efficient calorie burning.
· Emphasize Protein: Protein is a crucial component of a metabolism-boosting diet. It helps repair and build tissues, supports immune function, and contributes to a feeling of fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating. Include lean protein sources such as poultry, fish, lean meats, tofu, legumes, and dairy products in your meals.
· Prioritize Fiber: Fiber-rich foods support digestion and help regulate blood sugar levels. They also contribute to a feeling of satiety, preventing excessive calorie consumption. Aim to include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds in your diet to increase fiber intake.
· Opt for Whole Grains: Whole grains are an excellent source of sustained energy and are more nutrient-rich than refined grains. Foods like brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat bread offer essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, promoting healthy metabolism and overall well-being.
· Limit Added Sugars and Processed Foods: Minimize the consumption of added sugars and processed foods, as they often provide empty calories with little nutritional value. These types of foods can lead to energy fluctuations and hinder weight management efforts.
· Stay Hydrated: Drinking adequate water throughout the day supports metabolic processes and can help control appetite. Sometimes thirst can be mistaken for hunger, leading to unnecessary calorie intake.
· Mindful Eating: Pay attention to portion sizes and eat mindfully, savoring each bite and recognizing when you are comfortably full. Avoid distractions like television or phones during meals to stay connected to your body's hunger and satiety cues.
· Balance Macronutrients: Strive for a balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats to provide a steady energy source and support overall metabolic function.
· Eat Regularly: Avoid skipping meals and try to eat at regular intervals. Eating consistent meals and snacks throughout the day helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and supports a well-regulated metabolism.
Nourishing your body with nutrient-dense foods lays the foundation for long-term health and vitality. Consult a registered dietitian for personalized guidance and support if you have specific dietary concerns or weight management goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, metabolism is critical in body weight regulation and overall health. Understanding the scientific principles behind metabolism empowers individuals to take charge of their well-being and make informed decisions about their diet and lifestyle. Adopting positive habits that support overall metabolic health is essential to maintain a healthy metabolism.
At Cura4U, we are dedicated to providing a range of healthcare services to support individuals on their journey to better health. Our platform offers access to valuable medical information, lab tests, radiology services, and doctor consultations, enabling users to make well-informed decisions about their health. Individuals can nurture a healthy metabolism by emphasizing a balanced diet filled with nutrient-dense foods, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress effectively, and prioritizing sufficient sleep. When incorporated into daily life, these practices can lead to long-term weight management and overall improvement in health and well-being.
Take charge of your health with Cura4U's comprehensive healthcare services. Book lab tests, consult medical professionals, and access essential information to support your metabolic health journey. Start your path toward a healthier life today!
Our clinical experts continually monitor the health and medical content posted on CURA4U, and we update our blogs and articles when new information becomes available. Last reviewed by Dr. Saad Zia on July 24th, 2023.
References
Metabolism and weight loss: How you burn calories - Mayo Clinic- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/metabolism/art-20046508
Physiology, Metabolism - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov)- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546690/
Metabolism: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002257.htm
Metabolism - PMC (nih.gov)- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7545035/
Science of Metabolism (news-medical.net)- https://www.news-medical.net/health/Science-of-Metabolism.aspx
Metabolism: What It Does, What Affects It, and More (webmd.com)- https://www.webmd.com/fitness-exercise/what-is-metabolism
The truth about metabolism - Harvard Health- https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/the-truth-about-metabolism
10_Metabolism_and_energy.pdf (rsb.org.uk)- https://www.rsb.org.uk/images/10_Metabolism_and_energy.pdf
11 natural ways to increase your metabolism (medicalnewstoday.com)- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323328
Home Page: Metabolism - Clinical and Experimental (metabolismjournal.com)- https://www.metabolismjournal.com/
Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism (jofem.org)- https://www.jofem.org/
American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism -https://journals.physiology.org/journal/ajpendo
Catabolism vs. Anabolism: Hormones, Body Weight, and Exercises (healthline.com)- https://www.healthline.com/health/catabolism-vs-anabolism
Can you boost your metabolism?: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia-https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000893.htm


















