Vaginal yeast infections are a common health issue that affects millions of women worldwide. Although many women have experienced a yeast infection at some point in their lives, the topic can still be difficult to discuss and understand. This post aims to break through the barriers of discomfort and confusion surrounding this common issue. By delving into every aspect of vaginal yeast infections, from their causes and symptoms to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention, we aspire to empower women with comprehensive knowledge about their bodies.
Introduction to Vaginal Yeast Infections: A Brief Overview
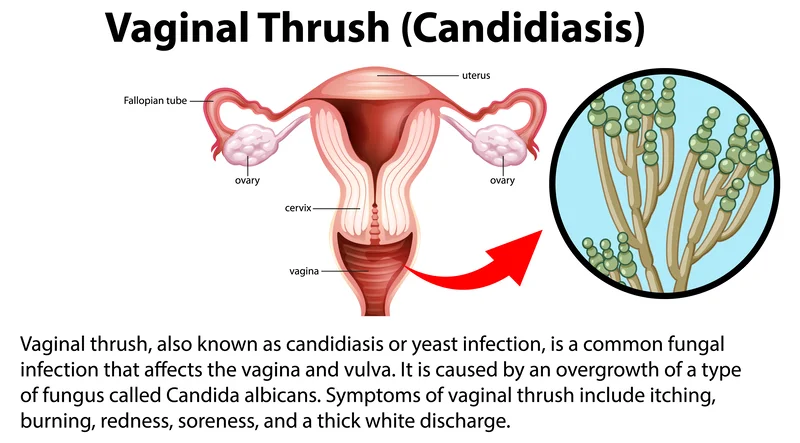
A vaginal yeast infection, medically referred to as vaginal candidiasis (vaginal thrush), stands as a common and often uncomfortable condition that targets the vaginal area. The primary culprit behind this condition is an overgrowth of Candida fungi (Candida albicans), which, under normal circumstances, exists in the vaginal region in limited quantities. Delving into the intricacies of this condition requires a deeper understanding of the delicate equilibrium maintained by a variety of microorganisms, including bacteria and yeast, within the vaginal environment. The vagina is home to a complex ecosystem where various microorganisms coexist harmoniously. Among these, Candida is a type of yeast that plays a natural role in maintaining balance. However, when this equilibrium is disrupted, Candida can undergo rapid multiplication, leading to an overabundance that sparks the onset of a yeast infection. Several factors can contribute to the disturbance of the vaginal microbiota and pave the way for the overgrowth of Candida. By understanding the factors that can disrupt this delicate balance, individuals can adopt proactive measures to prevent and manage yeast infections effectively, promoting overall vaginal health and well-being.
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors: Unraveling the Roots of Vaginal Yeast Infections
The development of a vaginal yeast infection is often influenced by a myriad of factors, each contributing to the delicate balance within the vaginal ecosystem.
Weakened Immune System: A weakened immune system stands as a significant contributor, rendering the body less capable of maintaining the natural equilibrium of microorganisms in the vaginal area. When the immune system is compromised, opportunistic pathogens like Candida can flourish, leading to overgrowth and subsequent infection.
Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes play a pivotal role in the susceptibility to yeast infections. Fluctuations in hormone levels, whether due to natural processes like menstruation, pregnancy, or the use of hormonal contraceptives, can disrupt the intricate balance of the vaginal microbiota. This imbalance creates an environment where Candida can thrive, initiating the onset of an infection.
Antibiotic Use: The use of antibiotics is another crucial factor in the development of yeast infections. While antibiotics are effective in treating bacterial infections, they can inadvertently eliminate not only harmful bacteria but also the beneficial ones that regulate the growth of yeast. This disruption in the delicate microbial balance paves the way for Candida overgrowth and infection.
Diabetes: Diabetes, especially when poorly controlled, poses a heightened risk for yeast infections. Elevated blood sugar levels create an environment conducive to yeast proliferation, making individuals with diabetes more susceptible to recurrent and persistent infections.
Pregnancy: Pregnancy introduces unique hormonal shifts and changes in the body that can increase the likelihood of yeast infections. The combination of hormonal fluctuations and potential changes in immune function during pregnancy creates conditions favorable to Candida overgrowth.
Hormonal Contraceptives: Women who use hormonal contraceptives or engage in frequent sexual activity may find themselves at an elevated risk of developing yeast infections. Hormonal contraceptives can influence the vaginal environment, while frequent sexual activity may disrupt the balance of microorganisms.
Clothing: Clothing choices also play a role in the development of yeast infections, with tight-fitting garments such as jeans or yoga pants creating a warm and moist environment. This environment becomes an ideal breeding ground for yeast, facilitating its rapid growth and increasing the likelihood of infection.
Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle factors, including diet and stress, add another layer of complexity to the multifaceted origins of yeast infections. A diet high in sugars and refined carbohydrates can contribute to elevated blood sugar levels, promoting conditions favorable for yeast growth. Stress, by impacting the immune system and hormonal balance, can further tip the scales toward an increased susceptibility to yeast infections.
In unraveling the roots of vaginal yeast infections, it becomes evident that a holistic understanding of the interconnected factors at play is essential. By addressing these various elements, individuals can adopt preventive measures and lifestyle adjustments to mitigate the risk of yeast infections, ultimately promoting a healthier and more resilient vaginal environment.
Signs and Symptoms: Decoding the Language of Vaginal Yeast Infections
Yeast infections manifest with a spectrum of symptoms, the severity and duration of which can vary among individuals. Recognizing these signs is pivotal for prompt intervention and effective management. Among the most prevalent and identifiable symptoms are itching, burning sensations, and redness in the vaginal area. These discomforts arise due to the overgrowth of Candida, which triggers irritation and inflammation in the sensitive tissues of the vagina.
A hallmark indicator of a yeast infection is the presence of a distinctive discharge, often likened to cottage cheese in texture. This discharge is typically thick and white, signifying the abundance of Candida organisms. The consistency and appearance serve as key diagnostic clues for healthcare professionals in confirming the presence of a yeast infection.
For some individuals, the impact extends beyond mere discomfort, as pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse or urination may accompany the infection. These sensations arise from the heightened sensitivity of inflamed tissues, adding to the overall distress experienced by affected individuals.
In more severe cases, yeast infections can lead to the development of skin cracks or sores in the vaginal area. This escalation of symptoms underscores the importance of timely intervention, as persistent or worsening conditions may require more targeted and intensive treatment approaches. Acknowledging the potential recurrence of these symptoms is crucial for proactive management. Individuals who have experienced a yeast infection should be attuned to any subtle signs of its resurgence, enabling them to seek prompt medical attention and avoid exacerbating symptoms. It is essential to recognize the diversity in how symptoms may present among different individuals. While the classic symptoms of itching, burning, redness, and discharge are common, variations exist. Some individuals may experience milder symptoms that are easily overlooked, emphasizing the need for heightened awareness and personalized attention to one's own body.
Understanding these individual differences in symptom presentation enhances the ability to seek timely and effective treatment. Since yeast infections share symptoms with other vaginal conditions, such as bacterial vaginosis or sexually transmitted infections, a nuanced understanding of the specific manifestations aids in accurate diagnosis and targeted therapeutic interventions.
Diagnosis Demystified: How Healthcare Professionals Identify Yeast Infections
The process of diagnosing yeast infections is a nuanced and thorough endeavor, encompassing various elements to ensure precision and efficacy. Healthcare professionals utilize a multifaceted approach involving clinical assessments and diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of Candida. Here's an insight into the demystification of the diagnosis process:
Physical Examination: A crucial first step in the diagnostic journey involves a thorough physical examination by a healthcare provider. This examination typically focuses on the genital area and may include an assessment of external symptoms like itching, redness, and swelling. Internal examinations may also be conducted to evaluate the state of the vaginal walls and the presence of any unusual discharge.
Symptom Discussion: Open communication between the healthcare provider and the individual is paramount. A detailed discussion about the nature and duration of symptoms and any potential contributing factors helps paint a comprehensive picture. This exchange of information aids in distinguishing yeast infections from other vaginal conditions with similar symptoms.
Laboratory Tests: Healthcare professionals often employ laboratory tests to confirm the diagnosis. Swabs or cultures may be taken from the vaginal area to collect samples of discharge. These samples are then analyzed to identify the presence of Candida or other microorganisms. Laboratory tests provide a more concrete understanding of the microbial composition, guiding accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Microscopic Examination: In some cases, a microscopic examination of the collected samples may be performed. This involves scrutinizing the samples under a microscope to detect the characteristic appearance of Candida yeast cells. This microscopic analysis adds another layer of confirmation to the diagnostic process.
Seeking professional confirmation of a potential yeast infection is crucial. While over-the-counter antifungal medications are available, accurate diagnosis by a healthcare provider ensures that the chosen treatment is appropriate for the specific type and severity of the infection, ultimately paving the way for timely and effective management of yeast infections.

Exploring the Conventional Approaches to Yeast Infections
Treatment approaches to Yeast Infections involve a multifaceted strategy, primarily centered around antifungal medications. This cornerstone in conventional treatment has demonstrated effectiveness in eliminating the overgrowth of Candida fungi and resolving infections. Antifungal medications, available in diverse forms such as oral tablets, topical creams, and suppositories, serve as the primary defense against yeast infections. Whether administered orally or applied directly to the affected area, these medications target and neutralize the Candida fungi responsible for the infection, leading to a swift resolution within a few days.
Ensuring the success of the treatment requires individuals to complete the full course of the prescribed medication, even if symptoms alleviate earlier. This comprehensive approach is crucial for eradicating any remaining Candida organisms and reducing the likelihood of recurrence. Premature discontinuation of treatment may contribute to incomplete resolution and potential relapse.
Open communication with healthcare providers is paramount throughout the treatment process. Individuals are encouraged to discuss any concerns or potential side effects with their healthcare professionals. While antifungal medications are generally safe, some women may experience side effects like nausea or diarrhea. Timely consultation enables healthcare providers to address these issues and, if necessary, adjust the treatment plan for optimal results.
Special considerations apply to pregnant or breastfeeding women, who should exercise caution and consult their healthcare provider before using antifungal medication. Although certain antifungal medications are considered safe during pregnancy, professional guidance ensures that the chosen treatment aligns with the unique considerations of this period.
Regular monitoring and follow-up assessments with healthcare providers are recommended to track treatment progress and address any concerns. These check-ins provide an opportunity to discuss lingering symptoms, address concerns, and ensure that the chosen treatment approach remains effective over time. This comprehensive approach to conventional treatments for yeast infections emphasizes the importance of a holistic and communicative strategy for optimal outcomes.
Prevention Strategies: Tips for Minimizing the Risk of Recurrent Yeast Infections
Minimizing the risk of recurrent yeast infections involves adopting proactive measures that prioritize good vaginal health and mitigate potential triggers disrupting the delicate balance of bacteria and yeast in the vaginal area. Here are practical tips for preventing yeast infections:
Wearing Loose-Fitting Clothing: Opt for breathable, loose-fitting clothing, such as cotton underwear, to promote air circulation and discourage the warm, moist environment that fosters yeast growth. Avoiding tight-fitting pants and synthetic materials can contribute to maintaining a healthier vaginal environment.
Avoiding Scented Products: Steer clear of scented hygiene products, including soaps, tampons, and feminine sprays. Fragrances and chemicals in these products can disrupt the natural pH balance of the vagina, making it more susceptible to yeast overgrowth. Choose mild, unscented alternatives to minimize the risk when cleansing the genital area. Opt for gentle, pH-balanced cleansers to maintain a healthy environment without causing irritation.
Avoiding Wet Clothing: Promptly change out of wet clothing, including swimsuits and workout gear. Lingering in damp or wet clothing creates an environment conducive to yeast growth. By changing into dry clothes promptly, you reduce the likelihood of developing conditions favorable to the development of infections.
Sexual Practices: Be mindful of sexual practices and their potential impact on vaginal health. Practices that introduce foreign substances or disrupt the natural pH balance, such as certain lubricants or spermicides, may increase the risk of yeast infections. Communicate with your partner about any sensitivities or concerns to ensure mutual understanding. Safe sex practices are essential for preventing the transmission of infections, including sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and conditions that can disrupt the vaginal microbiota. Proper use of barrier methods, such as condoms, and open communication with sexual partners contribute to overall sexual health.
Partner Communication: Open communication with sexual partners is key. If recurrent yeast infections are a concern, discussing preventive measures and being aware of potential factors contributing to the infections can help both partners make informed choices that support overall vaginal health.
Proper Hygiene Practices: Adopt proper hygiene practices, including wiping from front to back after using the toilet. This helps prevent the transfer of bacteria from the anal region to the vagina, reducing the risk of infections.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can have profound effects on the body, including the immune system. High-stress levels may compromise immune function, making the body more susceptible to infections, including yeast infections. Adopting stress management techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, or activities like yoga can contribute to a more balanced stress response.
Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep is fundamental to overall health, and its impact extends to immune function. During sleep, the body undergoes essential processes for repair and rejuvenation, including strengthening the immune system. Consistently getting enough restorative sleep supports the body's ability to ward off infections and contributes to a healthier vaginal environment.
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity is associated with numerous health benefits, including immune system support. Exercise promotes circulation, reduces inflammation, and contributes to overall well-being. Incorporating moderate exercise into the routine, such as brisk walking, swimming, or yoga, can positively influence immune function and contribute to a healthier vaginal environment.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is linked to overall health, including vaginal health. Obesity has been associated with an increased risk of yeast infections. Adopting a lifestyle that supports weight management contributes to a more resilient immune system and a decreased likelihood of infections.
Hydration: Adequate hydration is crucial for general health and is directly linked to the well-being of the vaginal tissues. Staying well-hydrated ensures proper moisture levels, supporting the body's natural defenses against infections. It also aids in the elimination of toxins, contributing to overall vaginal health.
Limiting Alcohol and Tobacco Use: Excessive alcohol consumption and tobacco use can negatively impact immune function and overall health. Limiting or abstaining from these substances contributes to a healthier immune system, reducing the risk of infections, including yeast infections.
Regular Health Check-ups: Regular gynecological check-ups and screenings are crucial for monitoring and maintaining vaginal health. These appointments provide an opportunity to address any concerns, receive guidance on preventive measures, and detect potential issues early.
Cultivating habits that support comprehensive vaginal health involves a holistic approach that encompasses various aspects of lifestyle. By integrating these prevention strategies into daily habits, individuals can take a proactive stance in minimizing the risk of recurrent yeast infections.
The Role of Diet: How Nutrition Impacts Vaginal Yeast Infections
Diet stands as a pivotal factor in nurturing the health of the vaginal area and mitigating the risk of yeast infections. Adopting a balanced and nutrient-rich diet plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system and fostering an environment that is less conducive to the overgrowth of Candida fungi. Here's an exploration of how nutrition impacts vaginal health:
Balanced Diet and Immune Support: A well-rounded and nutrient-rich diet, particularly one abundant in vitamins A and C, contributes to robust immune system function. These vitamins play key roles in maintaining the body's defenses against infections, including those that affect the delicate balance of microorganisms in the vaginal area. Incorporating fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into the diet ensures various nutrients essential for overall health.
Hydration and Vaginal Health: Adequate hydration is fundamental to overall health, and its impact extends to vaginal health. Staying well-hydrated supports the body's natural detoxification processes and helps maintain optimal moisture levels in the vaginal tissues. Proper hydration is a cornerstone of a holistic approach to promoting a healthy and well-lubricated vaginal environment.
Reducing Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates: One of the key dietary considerations for preventing yeast infections is minimizing the intake of sugar and refined carbohydrates. Candida fungi thrive on sugar, and an excess of it in the diet can contribute to their overgrowth. By reducing or eliminating sugary and refined carbohydrate-rich foods, individuals can create an environment less favorable for Candida, thereby decreasing the risk of yeast infections.
Probiotic-Rich Foods: Probiotics, beneficial bacteria that support a healthy microbial balance, can be incorporated into the diet through foods like yogurt with live cultures, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi. These foods contribute to the maintenance of a diverse and beneficial microbial community, both in the gut and the vaginal area.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, have anti-inflammatory properties that can positively influence overall immune function. Including sources of omega-3 fatty acids in the diet contributes to a balanced inflammatory response, potentially reducing the likelihood of inflammatory conditions that may impact vaginal health.
Whole Foods and Fiber: Emphasizing whole foods and dietary fiber supports gut health, which is interconnected with vaginal health. A fiber-rich diet promotes regular bowel movements, aiding in eliminating waste and potential irritants. This, in turn, contributes to a healthier overall microbial balance.
Limiting Processed Foods: Processed foods, often high in additives, preservatives, and artificial ingredients, may negatively impact overall health and immune function. Opting for whole, minimally processed foods ensures a more natural and nourishing approach to supporting the body's defenses.
By recognizing the interconnectedness of nutrition and vaginal health, individuals can empower themselves to make informed dietary choices that foster overall well-being.
Beyond Medications: Holistic and Natural Remedies for Vaginal Yeast Infections
Delving into holistic and natural remedies for vaginal yeast infections, we aim to shed light on potential complements to traditional treatments. It is imperative, however, to underscore that these approaches currently lack conclusive scientific evidence and formal trials. Therefore, individuals are strongly advised to approach these remedies with caution and prioritize seeking professional medical advice, particularly if they are pregnant, breastfeeding, or managing underlying health conditions.
Probiotics: Probiotics, or "good" bacteria, may contribute to restoring a healthy microbial balance in the body. While incorporating probiotics into the routine can be considered, it is crucial to note that their effectiveness in treating yeast infections is not universally proven. Probiotics can be taken orally or applied topically, but consultation with a healthcare professional is advisable.
Garlic: Garlic, known for its antimicrobial properties, is explored for its potential in combating fungal infections. Applying crushed garlic or garlic oil topically is a popular remedy, but its efficacy lacks robust scientific validation. Moreover, incorporating garlic into the diet should be done cautiously, and individuals should be aware of potential side effects.
Tea Tree Oil: With antimicrobial properties, tea tree oil is suggested as a natural antifungal remedy. However, caution is warranted, as it can be potent and may cause irritation. Proper dilution and patch testing are recommended, and individuals with sensitivities should avoid its use. Professional guidance is crucial before incorporating tea tree oil into a treatment regimen.
Boric Acid: Boric acid, available in suppository form, is considered for its antifungal properties. While it may be effective, its use should be under the guidance of a healthcare professional due to potential side effects. Improper use or excessive amounts may lead to complications, emphasizing the importance of professional oversight.
Yogurt: Yogurt, especially with live cultures like Lactobacillus acidophilus, is suggested as a natural remedy. While it may promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, its effectiveness is not universally established. Individuals should consult healthcare providers before using yogurt as a remedy, and those with lactose intolerance should be cautious.
These holistic remedies may offer relief for some individuals, but their use should not replace professional medical advice. Every person's health situation is unique, and consultation with healthcare providers ensures safe and effective choices aligned with personal health needs. Additionally, individuals should be aware of potential side effects or allergic reactions associated with these natural remedies.
Conclusion
Overall, vaginal yeast infections are a common health issue that can be uncomfortable and disruptive. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies for yeast infections, women can take steps to maintain good vaginal health and reduce the risk of recurrent infections. Whether through traditional treatments or holistic remedies, addressing yeast infections in a comprehensive and proactive manner can help women feel more empowered, proactive, and confident in their bodies.
At Cura4U, we understand the significance of accessible and convenient healthcare, especially when it comes to sensitive issues like vaginal yeast infections. Our dedicated team of healthcare professionals is committed to providing support and expert guidance tailored to your unique health needs. Through our telemedicine consultations and an array of primary healthcare services, you can now receive personalized treatment plans from the comfort of your home. Whether navigating yeast infections or addressing other common health concerns, Cura4U is here to assist you every step of the way. Take the initiative towards managing your vaginal health by scheduling a telemedicine appointment with our experienced professionals at Cura4U today.
Our clinical experts continually monitor the health and medical content posted on CURA4U, and we update our blogs and articles when new information becomes available. Last reviewed by Dr. Tayyab Saeed Akhter on January 2nd, 2024.
References
Vaginal Candidiasis | Fungal Diseases | CDC
UpToDate- https://www.uptodate.com/contents/vaginal-yeast-infection-beyond-the-basics
Yeast Infection | Johns Hopkins Medicine- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/candidiasis-yeast-infection
Yeast Infection > Fact Sheets > Yale Medicine- https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditions/yeast-infection
Vaginal yeast infection (thrush): Overview - InformedHealth.org - NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov)- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK543220/
Vaginal Candidiasis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov)- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459317/
Vaginal Yeast Infection (Candidiasis) - Women's Health Issues - MSD Manual Consumer Version (msdmanuals.com)- https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/women-s-health-issues/vaginitis,-cervicitis,-and-pelvic-inflammatory-disease/vaginal-yeast-infection-candidiasis
Vaginal Yeast Infection - Harvard Health- https://www.health.harvard.edu/a_to_z/vaginal-yeast-infection-a-to-z
Vaginal yeast infections | Office on Women's Health (womenshealth.gov)- https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/vaginal-yeast-infections